SI base units
The seven SI base units are defined by products of powers of the SI defining constants.
Prior to 2019, the concept of base units and derived units was used to define the SI. These categories, although no longer essential in the SI, are maintained in view of their convenience and widespread use.
| Name | Symbol | Quantity | Defining constants |
| kilogram | kg | mass | h c−2 ΔνCs |
| The kilogram is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the Planck constant h to be 6.626 070 15 × 10−34 when expressed in the unit J s, which is equal to kg m2 s−1, where the metre and the second are defined in terms of c and ΔνCs. |  |
||
| 1 kg ≈ 1.475 521 399 735 270 916 × 1040 h c−2 ΔνCs | |||
| metre | m | length | c ΔνCs−1 |
| The metre is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the speed of light in vacuum c to be 299 792 458 when expressed in the unit m s−1, where the second is defined in terms of the caesium frequency ΔνCs. |  |
||
| 1 m ≈ 30.663 318 988 498 369 762 c ΔνCs−1 | |||
| second | s | time | ΔνCs−1 |
| The second is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency ΔνCs, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium 133 atom, to be 9 192 631 770 when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s-1. |  |
||
| 1 s = 9 192 631 770 ΔνCs−1 | |||
| ampere | A | electric current | ΔνCs e |
| The ampere is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the elementary charge e to be 1.602 176 634 × 10−19 when expressed in the unit C, which is equal to s A, where the second is defined in terms of ΔνCs. | 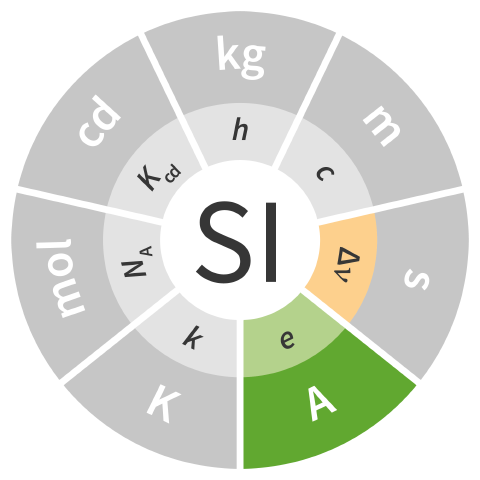 |
||
| 1 A ≈ 6.789 686 817 250 553 927 × 108 ΔνCs e | |||
| kelvin | K | thermodynamic temperature | h ΔνCs k−1 |
| The kelvin is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the Boltzmann constant k to be 1.380 649 × 10−23 when expressed in the unit J K−1, which is equal to kg m2 s−2 K−1, where the kilogram, metre and second are defined in terms of h, c and ΔνCs. | 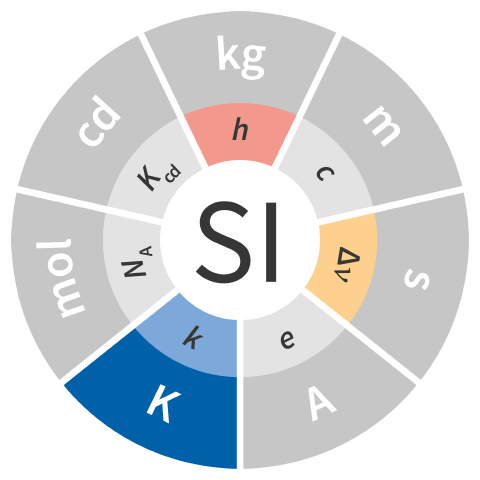 |
||
| 1 K ≈ 2.266 665 264 601 104 867 h ΔνCs k−1 | |||
| mole | mol | amount of substance | NA−1 |
| One mole contains exactly 6.022 140 76 × 1023 elementary entities. This number is the fixed numerical value of the Avogadro constant, NA, when expressed in the unit mol−1 and is called the Avogadro number. | 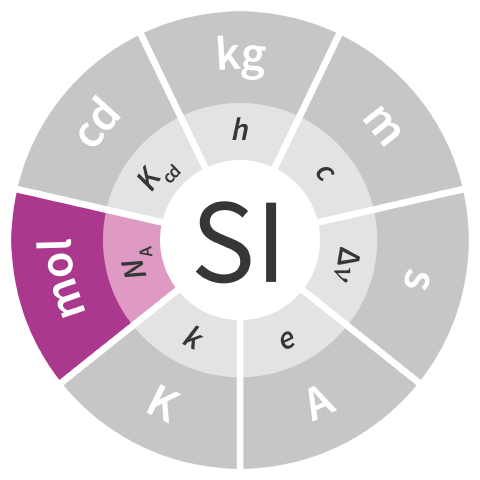 |
||
| 1 mol = 6.022 140 76 × 1023 NA−1 | |||
| candela | cd | luminous intensity | h ΔνCs2 Kcd |
| The candela, symbol cd, is the SI unit of luminous intensity in a given direction. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the luminous efficacy of monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 × 1012 Hz, Kcd, to be 683 when expressed in the unit lm W−1, which is equal to cd sr W−1, or cd sr kg−1 m−2 s3, where the kilogram, metre and second are defined in terms of h, c and ΔνCs. |  |
||
| 1 cd ≈ 2.614 830 482 285 616 × 1010 h ΔνCs2 Kcd | |||
All other SI units can be derived either from these seven base units, or directly from the seven SI defining constants.