joule per kelvin
SI coherent derived unit whose name and symbol includes an SI coherent derived unit with a special name and symbol
| Name | Symbol | Quantity | Base units |
| joule per kelvin | J/K | heat capacity, entropy | kg m2 s−2 K−1 |
 The joule per kelvin, symbol J/K, is the SI coherent derived unit of heat capacity, and entropy. The joule per kelvin, symbol J/K, is the SI coherent derived unit of heat capacity, and entropy.One joule per kelvin is equal to the heat capacity of an object that requires one joule of heat energy to raise its temperature by one kelvin. |
|||
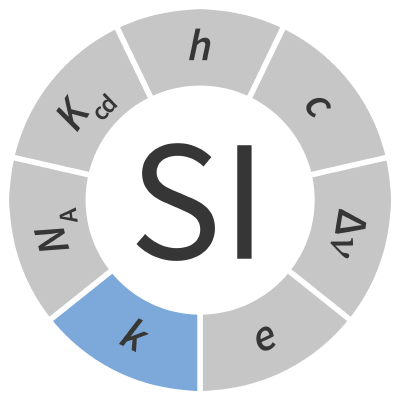
| Definition | k | ||
 |
|||
The fixed numerical value of the Boltzmann constant, k, is defined to be exactly 1.380 649 × 10‑23 when expressed in the unit joule per kelvin, symbol J K-1.
Inverting this relation gives an exact expression for the joule per kelvin in terms of the SI defining constant k :
The effect of this definition is that one joule per kelvin is exactly 1⁄1.380 649 × 10−23 of the Boltzmann constant.
Heat capacity
The amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of an object by one kelvin depends on the object’s substance. The amount of energy needed is also directly proportional to the amount of substance.
The amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of an object by one kelvin is equal to the heat capacity of the object.